Needle Stick Injury Kkm

G prevention of needle stick or sharps injuries.
Needle stick injury kkm. Health unit ministry of health from 1998 2005 needlestick injury is the major cause of injuries among the ministry of health personnel which contributes to a total of 74 9 of all injuries. It is estimated that 600 000 to 800 000 needlestick injuries occur per year in the united states 1. In response to the risk of exposure institutions have focused on primary prevention as a means of reducing the incidence of needlesticks and thereby decreasing the number of bloodborne pathogen transmissions. Evaluation of the needle stick injury for the appropriate use of pem should be initiated immediately.
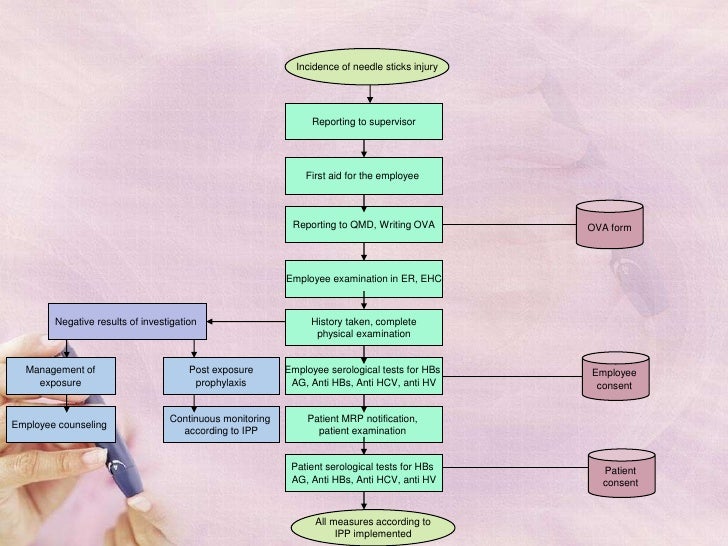
Management and notification of post occupational exposure to needle stick injury hypodermic and suture needle sharps blood blood products and body fluids among health care workers submission of report for cases of qap nsi. Includes health acts regulations circulars campaigns and online services. Provides profile programmes publications agencies and statistics. Infection prevention and control ipc measures in managing patient under investigation pui or confirmed coronavirus disease covid 19 this guidelineis based oncurrent informationavailable regarding disease severity transmission efficacy and shedding duration.
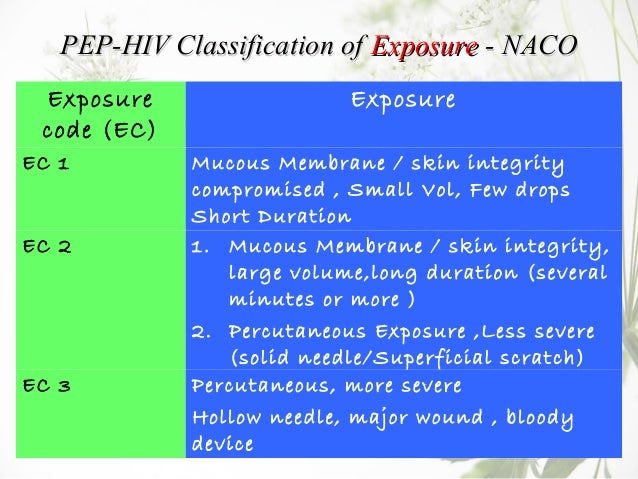
Community acquired needlestick injuries ca nsi in children are a cause of significant parental anxiety. The decision to initiate pem is based upon the nature of the needle stick injury severity of exposure and source patient sero status for hiv hepatitis b and hepatitis c and medication regimen if known 3. Including needle stick injuries and other incidents. Dr t v rao md exposures which place health personnel at risk of blood borne infection a percutaneous injury e g.
Needle stick injury nsi or cut with a sharp instrument contact with the mucous membrane of eye or mouth contact with non intact skin abraded skin or with dermatitis contact with intact skin when the duration of contact is prolonged with blood or other potential. It may reassure healthcare workers parents and patients that there are no published reports of an incidental ca nsi in a child such as might occur on the beach or in a park leading to transmission of a blood borne virus such as hepatitis b hepatitis c or hiv. Of these many if not most go unreported 2. It further notes that 37 6 of hepatitis b 39 of hepatitis c and 4 4 of hiv aids in health care workers around the world are due to needlestick injuries.
In the united states of america the u s centers for disease. Who reports in the world health report 2002 that of the 35 million health care workers 2 million experience percutaneous exposure to infectious diseases each year. Among the personnel nurses sustained the highest number of needlestick injuries.